Episode 3 The Rise of Islam and Europe’s Knights
The Middle Ages Around the World
Dr Joyce E Salisbury
Film Review
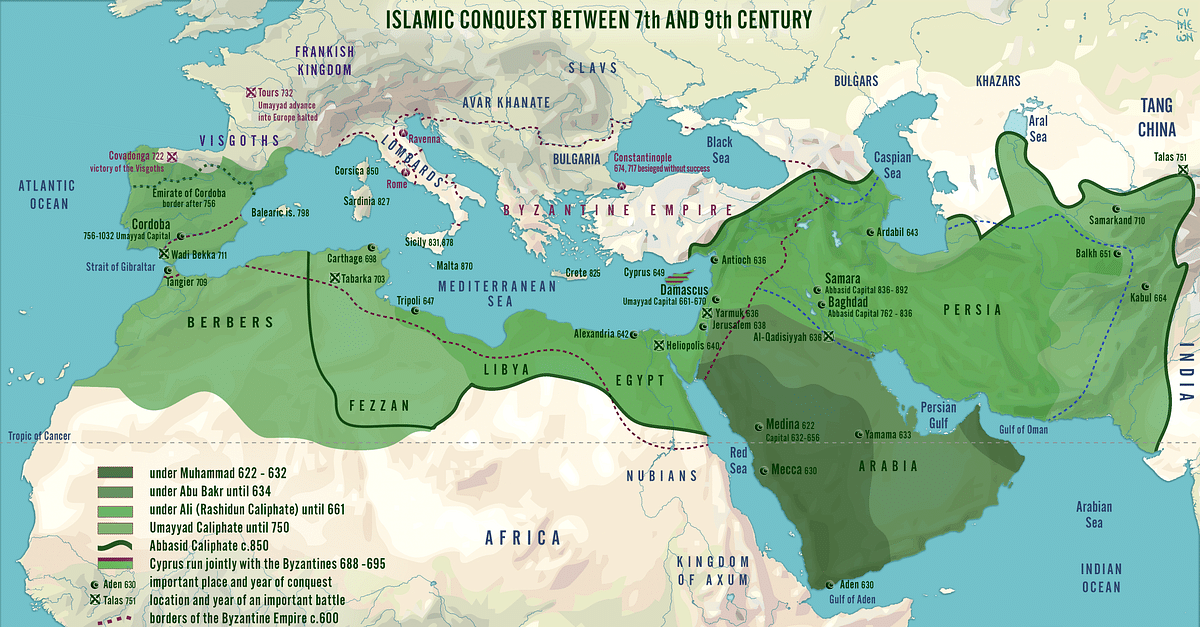
In 570 AD when the prophet Mohammad was born, the Arabian peninsula consisted of two coexisting cultures, city dwellers (mainly in coastal cities and strategic desert oases) and Bedouin nomads who worshiped nature and an ancient black meteorite installed in the Ka’aba shrine in Mecca.
An orphan, Mohammad was raised by a merchant uncle, becoming a merchant himself and marrying a wealthy widow (Kadija). He learned about monotheism from Jewish and Byzantine traders he traded with. Troubled by the religious conflict he encountered among monotheists, in 610 he experienced the first of 20 years of visitations from the angel Gabriel. The Koran is a record of thee visions.
Fellow merchants in Mecca heavily persecuted Mohammad’s early followers, worried they would disrupt the lucrative Bedouin pilgrimages to the Ka’aba. Following an assassination attempt in 622, he and his followers fled to Medina, where he converted Bedouin nomads.
In 630, he returned to Mecca with a force of 10,000 Bedouin followers, deciding to retain the shrine at Ka’aba as a sign from Allah.* He died in 632, appointing four caliphs to continue his mission of spreading of Islam to non-believers:
- 634 – Islamic forces from the Arabian peninsula attack and overrun Byzantium’s southern provinces.
- 636 – Islamic forces capture Mesopotamia.
- 639 – Islamic forces capture Palestine and Syria.
- 642 – Islamic forces was capture Egypt.
- 651 – Islamic forces capture Persia.
- 661, Islamic forces control entire Arabian peninsula.
- By 711, Islamic forces had conquered the Hindu kingdom in northwest India and a Berber Muslim convert had successfully invaded most of the Iberian peninsula.
- By 751, Muslim had seized all North African possessions of the Byzantine empire (causing them to lose essential grain imports).
Dr Salisbury attributes the early Muslims’ phenomenal military success to 1) the military prowess of their mounted Bedouin warriors and 2) their steadfast religious tolerance towards Christians and Jews (referred to as People of the Book). Although they required non-believers to pay a special tax, they were far more tolerant than the Byzantines and Visigoths. Both practiced ruthless repression against Jews and Christian who failed to follow prescribed beliefs.
Monopolizing the Silk Road Trade
After securing a monopoly over the Silk Road trade, Islamic leaders moved their capitol; from Mecca to Damascus (in 750) and from there to Baghdad in 762. The city’s growing prosperity led to the appearance of the world’s first bankers, to provide currency exchange and letters of credit. Meanwhile the city’s population grew to over one million in 50 years.
In 732 Muslim armies made an unsuccessful attempt to invade France. They were repelled by an army led by Charles Martel, the mayor of the palace (ie prime minister) of Austrasia, the eastern region of the Merovingian Frankish kingdom. Defeating the Muslims at the the Battle of Tours near Poitier, he forced their retreat across the Pyrenees.
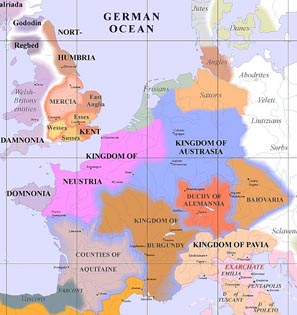
His son Pepin the Short, founder of the Carolingian dynasty, would reunify the Frankish kingdom. Although he recognized the need for a standing army to defend against further invasions, he lacked the trade income of the Muslims and Byzantines to fund one. Instead he established what is now known as the feudal system. In return for their military services, he awarded his knights a plot of land (and all the serfs living on it). Eventually all western kings, as well as the Byzantine empire, adopted this model of supporting standing armies.
*Which continues to this day as the annual Hajj or pilgrimage to the Ka’aba in Mecca.
**The western region was referred to as Neustria.
Film can be viewed free with a library card on Kanopy.
https://www.kanopy.com/en/pukeariki/watch/video/13172786/13172793
